Experiments to illustrate the resonance frequency in a quartz crystal microbalance with low cost materials
Downloads
- PDF (Español (España)) 451
- EPUB (Español (España)) 91
- VISOR (Español (España))
- MÓVIL (Español (España))
- XML (Español (España)) 74
DOI
https://doi.org/10.25267/Rev_Eureka_ensen_divulg_cienc.2024.v21.i2.2201Info
Abstract
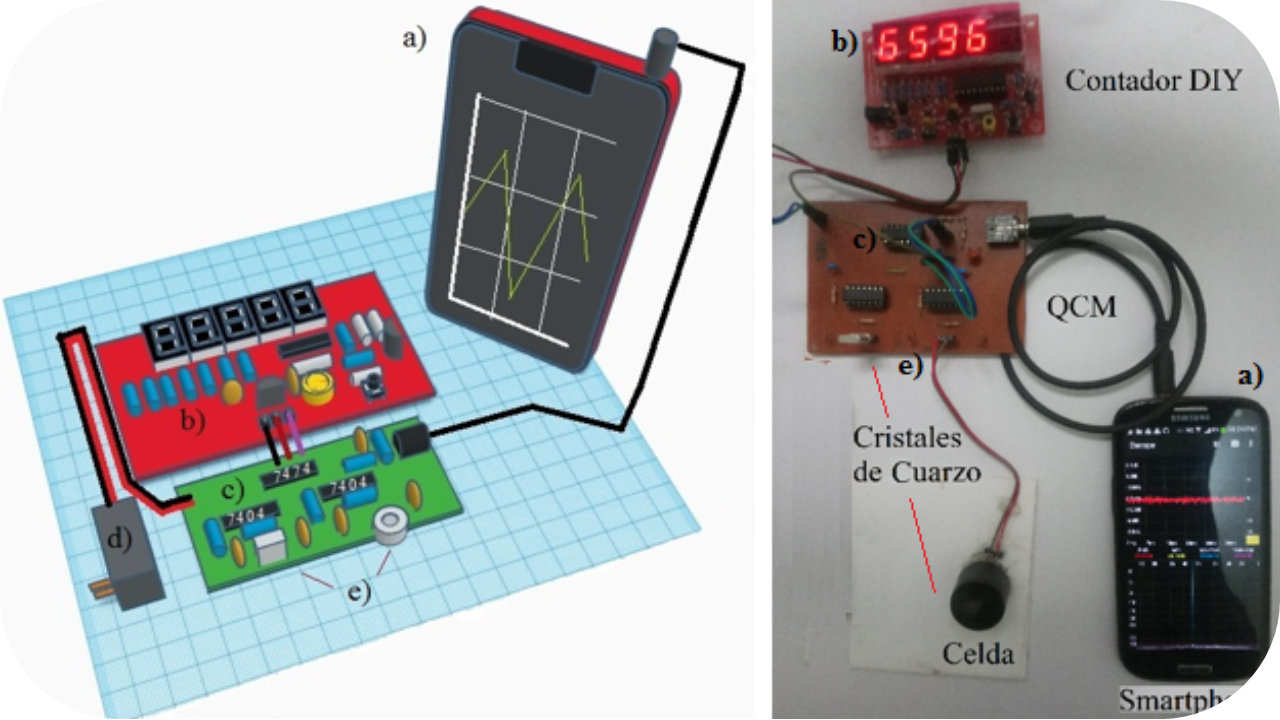
This study proposes three activities for a multidisciplinary laboratory practice with university students of advanced cycles, these didactic activities seek to develop scientific curiosity through the construction of an analytical instrument. To this end, students assemble a microbalance with low-cost frequency meters by replacing the oscilloscope with smartphones, DIY frequency counters, and Arduino development boards, for the educational purpose of illustrating the piezoelectric properties of quartz crystal and its relationship with the resonant frequency by experiential learning.
Keywords
Downloads
Supporting Agencies
How to Cite
License
Copyright (c) 2024 Julio David Gonzales Balladares, Evelyn Toque-Huamán

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License.
Require authors to agree to Copyright Notice as part of the submission process. This allow the / o authors / is non-commercial use of the work, including the right to place it in an open access archive. In addition, Creative Commons is available on flexible copyright licenses (Creative Commons).

Reconocimiento-NoComercial
CC BY-NC
References
Arnau, A. (2008). A Review of interface electronic systems for AT-cut quartz crystal microbalance applications in liquids. Sensors 8(1), 370-411. https://doi.org/10.3390/s8010370
Alassi, A., Benammar, M., Brett, D. (2017). Quartz crystal microbalance electronic interfacing systems: A review, Sensors. Sensor 17(12), 2799. https://doi.org/10.3390/s17122799
Bloom, B., Krathwohl, D. (1956). Taxonomy of educational objectives: The classification of educational goals. Handbook I: Cognitive domain. Nueva York, USA: Longmans, Green.
Bruckenstein, S., Shay, M. (1985). Experimental aspects of use of the quartz crystal microbalance in solution. Electrochimica Acta 30(10), 1295-1300, https://doi.org/10.1016/0013-4686(85)85005-2
Cady, W. G. (1946). Piezoelectricity : An introduction to the theory and applications of electromechanical phenomena in crystals. McGraw-Hill, New York.
Carvajal-Ahumada, L. A., Serrano, J. J., Pazos, J. E., García, M. A., Herrera, O. L. (2017). Diseño y evaluación de un micro viscosímetro de bajo costo utilizando un resonador de cristal de cuarzo y Arduino. Orinoquia 21(1), 45-55, https://doi.org/10.22579/20112629.430
Flores-Flores, E., Flores-Mena, J. E., Castillo, M. M. M., Arias, E. M. G., Mendoza-Álvarez, M. E., Alcántara-Iniesta, S. (2010). Construcción y caracterización eléctrica de una microbalanza con Bi4Ti3O1. Superficies y vacío 23(S), 153-160, https://www.redalyc.org/articulo.oa?id=94248264031
Jayasvasti, S., Isarakorn, D., Nundrakwang, S. (2017). Comparative study of QCM analyzers based on pierce oscillator and electromechanical impedance techniques. IEEE Conferences, 1, https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/7859608
Julian, T., Hidayat, N., Rianjanu, A., Dharmawan, A. B., Wasisto, H. S., Triyana, K. (2020). Intelligent mobile electronic nose system comprising a hybrid polymer-functionalized quartz crystal microbalance sensor array. ACS Omega 5(45), 29492-29503, https://doi.org/10.1021/acsomega.0c04433
Kamel, M. M., El-Nimr, M. K., Assar, S. T., Atlam, A. S. (2013). Design of a simple low-cost quartz crystal microbalance system. Instrumentation Science & Technology 41(5), 473-489, https://doi.org/10.1080/10739149.2013.792096
Kanazawa, K. K., Gordon II, J. G. (1985). The oscillation frequency of a quartz resonator in contact with liquid. Analytica Chimica Acta 175, 99-105, https://doi.org/10.1016/S0003-2670(00)82721-X
Li, F., Bao, Y., Wang, D., Wang, W., Niu, L. (2016). Smartphones for sensing. Science Bulletin 61(3), 190-201, https://doi.org/10.1007/s11434-015-0954-1
Meissner, D., Sarpong, D., Ofosu, G., Botchie, D. (2021). The rise of do-it-yourself (DiY) laboratories: Implications for science, technology, and innovation (STI) policy. Technological Forecasting and Social Change 165, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.techfore.2021.120589
Mista, C., Zalazar, M., Pealva, A., Martina, M., Reta, J. M. (2016). Open source quartz crystal microbalance with dissipation monitoring. Journal of Physics: Conference Series 705, https://doi.org/10.1088/1742-6596/705/1/012008
Nomura, T., Okuhara, M. (1982). Frequency shifts of piezoelectric quartz crystals immersed in organic liquids. Analytica Chimica Acta 142, 281-284, https://doi.org/10.1016/S0003-2670(01)95290-0
Rodahl, M., Höök, F., Krozer, A., Brzezinski, P., Kasemo, B. (1995). Quartz crystal microbalance setup for frequency and Q‐factor measurements in gaseous and liquid environments, Review of Scientific Instruments 66, 3924, https://doi.org/10.1063/1.1145396
Scheeline, A. (2010). Teaching, learning, and using spectroscopy with commercial, off the shelf technology. Applied Spectroscopy 64(9), 256A-268A. https://doi.org/10.1366/000370210792434378
Sauerbrey, G. (1959). Uso de cristales oscilantes para pesaje de capas delgadas y para micropesaje. Zeitschrift für Physik 155, 206-222. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01337937
Tomas-Serrano, A. (2021). Un experimento para ilustrar el primer principio de la termodinámica en bachillerato: creación de una nube de alcohol dentro de una botella. Revista Eureka sobre Enseñanza y Divulgación de las
Ciencias 18(3), 3401, https://doi.org/10.25267/Rev_Eureka_ensen_divulg_cienc.2021.v18.i3.3401
Wei, D. (2016). Tesis Master: Low-cost quartz crystal microbalance system platform designed for chemical nanoparticle, Kentucky, Western Kentucky University. https://digitalcommons.wku.edu/theses/1635/






